
Solutions to SQA examination
Higher Grade Physics
2000
Return to past paper index page.
Section A
1. C 11. A
2. D 12. B
3. D 13. A
4. B 14. D
5. E 15. A
6. D 16. C
7. A 17. C
8. A 18. E
9. D 19. B
10.E 20. C
Section B
21.a.i. Vhorizontal=Vresultantxcos60o
V=7xcos60o
Vhor=3.5(m/s)
a.ii.Vvertical=Vresultantxsin60o
Vver=7xsin30o
Vver=6.06(m/s)
b. The horizontal velocity throughout is constant. This fact can be used
to calculate the time to reach the dish.
t = shor/Vhor
t = 2.8/3.5
t = 0.8s
c. h = svert = ?
t = 0.8s
vvert = +6.06m/s
a = -9.8m/s2
sver = ut + 1/2(at2)
sver = 6.06x0.8 + 1/2(-9.8x0.82)
sver = 1.71m
d. If the release point of the projectile is taken to be the ground line,
this means it will have no potential energy at this height. The total
energy on release is therefore all the kinetic energy.
Ek(initial) = Etotal
At height h the total energy of the projectile is made up of
potential energy(Ep) and kinetic energy(Ek).
Etotal = Ek + Ep
The kinetic energy of the projectile as it enters the dish must, therefore, be
less than that when it leaves the contestants hand.
22.a.i. Using equations of motion
u = 0m/s v2 = u212 + 2as
a = -9.8m/s2 v22 = 02 + 2x-9.8x-2
s = -2m v2 = 39.2(m/s)2
v = ? v = -6.26m/s (negative indicates downward direction)
Using conservation of energy
Ep = Ek
mgh = mv2/2
v2 = 2gh
v = SQRT(2gh)
v = SQRT(2x-9.8x-2)
v = SQRT(39.2)
v = -6.26m/s ...as before
a.ii.Favg = change in momentum/contact time
Favg = (mv-mu)/t
Favg = m(v-u)/t
Favg = 15(0-[-6.26])/0.02
Favg = 4695N
This is the force that decelerates the mass. The force exerted by the mass
on the pipe is equal an opposite.
Favg = -4695N
The negative sign indicates that the force acts in the downwards direction.
b. The thick layer of soft material will increase the time over which the
momentum changes. As the change in momentum is the same, the average
unbalanced force must be less.
c. Block X will cause more damage because the force, although the same for
each block, is exerted over a smaller area. This results in more pressure
applied to the pipe.
Pressure = Force/Area
23.a. The pressure on the lower surface is equal to that on the top surface
plus the additional fluid pressure.
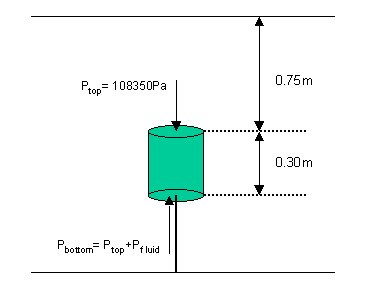 Pbottom = Ptop + rgh
Pbottom = (108350 + 1000x9.8x0.3)Pa
Pbottom = (108350 + 2940)Pa
Pbottom = 111290Pa
b.
Pbottom = Ptop + rgh
Pbottom = (108350 + 1000x9.8x0.3)Pa
Pbottom = (108350 + 2940)Pa
Pbottom = 111290Pa
b.
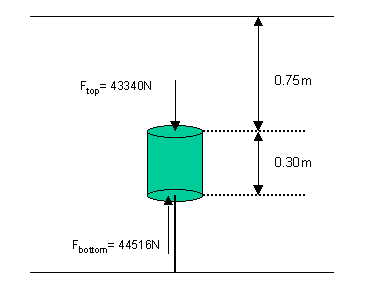 Fupthrust = Fbottom-Ftop
Fbottom = PbottomA
Fbottom = 111290x0.4 = 44516N
Ftop = PtopA
Ftop = 108350x0.4 = 43340N
Fupthrust = 44516-43340
Fupthrust = 1176N
c. As the density of sea water is greater than that of fresh water, the additional
pressure, due to the fluid, acting on the lower surface will increase. This
will increase the upthrust.
24.a. To calculate the capacitance use the mean values of charge and voltage.
C = Q/V
C = (32/2.56)mF
C=12.5mF
The percentage error in capacitance value can be taken to be equal
to that of largest individual percentage error.
% error in voltage = (0.01/2.56)x100 = 0.39%
% error in charge = (1/32)x100 = 3.125%
C=12.5mF+-3.125%
OR
3.125% of 12.5mF = 0.39mF
=> C = (12.5+-0.4)mF
NB/
Only quote the error to the same number of decimal places as the
capacitance value.
b.i. The maximum energy is stored in the capacitor when the voltage across
the capacitor is equal to the supply voltage.
Vc= 12V
C = 2200x10-6
E = ?
E = 1/2(QVc)
Q = CVc
=>E = 1/2(CVc2)
E = 0.5(2200x10-6x122)
E = 0.1584J
b.ii.(A) When the switch is opened the capacitor discharges through the
resistor and relay coil. The discharge current magnetises the
coil closing the switch in the lamp circuit, causing the lamp
to light. As the discharge current gradually falls the coil loses
its magnetism and the switch in the lamp circuit opens. When this
happens the lamp goes off.
(B) Increasing the value of the capacitor increases the discharge
time. The energy stored in the capacitor is also greater. This
means that the lamp will stay lit for longer.
25.a.i. When used to produce a voltage the diode is said to be in
photo voltaic mode.
a.ii. Light produces electron hole pairs in the depletion layer
of the pn-junction.
a.iii.The voltmeter reading increases as the intensity of the
light increases.
b.i. The emf is equal to the open circuit voltage.
emf = 0.508V
b.ii. r = Vlost/I
r = (0.508-0.040)/1.08x10-3
r = 0.468/1.08x10-3
r = 433.3W
Note: The answer to part (b.ii.) is too high to be realistic.
For this reason a correction was made to the values used
during the exam. However, the above answer does not use
the corrected value.
c. Decreasing the value of the load resistor will increase the current
in the circuit. This will increase the "lost" volts (Vlost=Ir).
Voltmeter reading = emf-Vlost
This explains the lower reading on the voltmeter when the switch is closed.
26.a.i. Period(T) = 4x2.5ms = 10ms
frequency(f) = 1/T
f = 1/10x10-3
f = 100Hz
a.ii. Vpeak = 2x5 = 10V
Vrms = Vpeak/SQRT2
Vrms = 10/1.414
Vrms = 7.07V
Irms = Vrms/R
Irms = 7.07/200
Vrms = 0.035A
b. The amplitude of the voltage across the resistor is reduced
because there is a voltage drop across the diode.
The negative half of the voltage cycle is removed because
the diode only conducts when it is forward biased.
27.a. The intensity of radiation is equal to the incident power per unit area.
I = P/A
b. By keeping the light meter a constant distance from X you are
justified in stating that any change in the recorded intensity
is a result of changing q. If the distance was altered a change
in intensity could be the result of a diverging beam.
c.i. The critical angle is found by noting the incident angle at which
the reflected intensity reaches a maximum.
q = 42o
c.ii. nglass = 1/sinqcritical
nglass = 1/sin42o
nglass = 1.49
c.iii.The intensity of ray T will decrease as angle q is increased upto 42o.
At angles equal to and above 42o the intensity of ray T will fall
to zero, as the incident ray will be totally internally reflected.
28.a.i. Photoelectric emission is the term used to describe the process by which
an electron bound in an atom can absorb enough energy from a single photon
to escape, or be emitted, from the atom.
a.ii. Threshold frequency
a.iii.As the intensity of the radiation is increased there are more incident
photons on the metal. Consequently, more electrons can absorb energy
from the incident radiation. This will result in more emitted electrons
which is consistent with the increased current.
28.b.i. Ephoton = hf
Ephoton = 6.63x10-34x9.0x1014
Ephoton = 5.967x10-19J
b.ii. Etotal = NEphoton
N = Etotal/Ephoton
N = 40.5x10-6/5.967x10-19
N = 6.79x1013
OR (If you like doing things the hard way.)
I = P/A
I = (Etotal/t)/A
I = (NEphoton/t)/A
=>N = AIt/Ephoton
=>N = (1.8x10-9x25x15x60)/ 5.967x10-19
=>N = 4.05x10-5/5.967x10-19
=>N = 6.79x1013
b.iii.The time taken for sunlight to erase the chip will be greater.
This is because only a proportion of the 25W/m2 from sunlight is
ultraviolet and it would therefore take longer for the semiconductor
to absorb the required number of photons.
29.a.i. To calculate x and y use conservation of atomic and mass number.
Atomic Number
Total LHS = Total RHS
88 = y + 2
y = 88 - 2
y = 86
Mass Number
Total LHS = Total RHS
226 = x + 4
x = 226 - 4
x = 222
222
Rn
86
a.ii. Energy is released in this reaction because the mass
of the products is less than that of the radium nucleus.
a.iii.Mass LHS
3.75428x10-25kg
Mass RHS
(3.68771x10-25 + 6.64832x10-27)kg = 3.7541932x10-25kg
Mass defect(DM) = Mass LHS - Mass RHS
DM = 3.75428x10-25 - 3.7541932x10-25
DM = 8.68x10-30kg
E = DMC2
E = 8.68x10-30x(3x108)2
E = 7.812x10-13J
b. Ekfinal = Ekinitial + Ekgain
Ekfinal = 1/2[mvinitial2]
Ekfinal = 1/2[6.64832x10-27x(1.5x107)2]
Ekfinal = 7.47936x10-13J
Ekgain = qV
q = charge on alpha particle = +2e = 2x1.6x10-19 = 3.2x10-19C
V = accelerating potential difference = 25kV
Ekgain = 3.2x10-19x25000
Ekgain = 8x10-15J
Ekfinal = 7.47936x10-13 + 8x10-15
Ekfinal = 7.55936x10-13J
Fupthrust = Fbottom-Ftop
Fbottom = PbottomA
Fbottom = 111290x0.4 = 44516N
Ftop = PtopA
Ftop = 108350x0.4 = 43340N
Fupthrust = 44516-43340
Fupthrust = 1176N
c. As the density of sea water is greater than that of fresh water, the additional
pressure, due to the fluid, acting on the lower surface will increase. This
will increase the upthrust.
24.a. To calculate the capacitance use the mean values of charge and voltage.
C = Q/V
C = (32/2.56)mF
C=12.5mF
The percentage error in capacitance value can be taken to be equal
to that of largest individual percentage error.
% error in voltage = (0.01/2.56)x100 = 0.39%
% error in charge = (1/32)x100 = 3.125%
C=12.5mF+-3.125%
OR
3.125% of 12.5mF = 0.39mF
=> C = (12.5+-0.4)mF
NB/
Only quote the error to the same number of decimal places as the
capacitance value.
b.i. The maximum energy is stored in the capacitor when the voltage across
the capacitor is equal to the supply voltage.
Vc= 12V
C = 2200x10-6
E = ?
E = 1/2(QVc)
Q = CVc
=>E = 1/2(CVc2)
E = 0.5(2200x10-6x122)
E = 0.1584J
b.ii.(A) When the switch is opened the capacitor discharges through the
resistor and relay coil. The discharge current magnetises the
coil closing the switch in the lamp circuit, causing the lamp
to light. As the discharge current gradually falls the coil loses
its magnetism and the switch in the lamp circuit opens. When this
happens the lamp goes off.
(B) Increasing the value of the capacitor increases the discharge
time. The energy stored in the capacitor is also greater. This
means that the lamp will stay lit for longer.
25.a.i. When used to produce a voltage the diode is said to be in
photo voltaic mode.
a.ii. Light produces electron hole pairs in the depletion layer
of the pn-junction.
a.iii.The voltmeter reading increases as the intensity of the
light increases.
b.i. The emf is equal to the open circuit voltage.
emf = 0.508V
b.ii. r = Vlost/I
r = (0.508-0.040)/1.08x10-3
r = 0.468/1.08x10-3
r = 433.3W
Note: The answer to part (b.ii.) is too high to be realistic.
For this reason a correction was made to the values used
during the exam. However, the above answer does not use
the corrected value.
c. Decreasing the value of the load resistor will increase the current
in the circuit. This will increase the "lost" volts (Vlost=Ir).
Voltmeter reading = emf-Vlost
This explains the lower reading on the voltmeter when the switch is closed.
26.a.i. Period(T) = 4x2.5ms = 10ms
frequency(f) = 1/T
f = 1/10x10-3
f = 100Hz
a.ii. Vpeak = 2x5 = 10V
Vrms = Vpeak/SQRT2
Vrms = 10/1.414
Vrms = 7.07V
Irms = Vrms/R
Irms = 7.07/200
Vrms = 0.035A
b. The amplitude of the voltage across the resistor is reduced
because there is a voltage drop across the diode.
The negative half of the voltage cycle is removed because
the diode only conducts when it is forward biased.
27.a. The intensity of radiation is equal to the incident power per unit area.
I = P/A
b. By keeping the light meter a constant distance from X you are
justified in stating that any change in the recorded intensity
is a result of changing q. If the distance was altered a change
in intensity could be the result of a diverging beam.
c.i. The critical angle is found by noting the incident angle at which
the reflected intensity reaches a maximum.
q = 42o
c.ii. nglass = 1/sinqcritical
nglass = 1/sin42o
nglass = 1.49
c.iii.The intensity of ray T will decrease as angle q is increased upto 42o.
At angles equal to and above 42o the intensity of ray T will fall
to zero, as the incident ray will be totally internally reflected.
28.a.i. Photoelectric emission is the term used to describe the process by which
an electron bound in an atom can absorb enough energy from a single photon
to escape, or be emitted, from the atom.
a.ii. Threshold frequency
a.iii.As the intensity of the radiation is increased there are more incident
photons on the metal. Consequently, more electrons can absorb energy
from the incident radiation. This will result in more emitted electrons
which is consistent with the increased current.
28.b.i. Ephoton = hf
Ephoton = 6.63x10-34x9.0x1014
Ephoton = 5.967x10-19J
b.ii. Etotal = NEphoton
N = Etotal/Ephoton
N = 40.5x10-6/5.967x10-19
N = 6.79x1013
OR (If you like doing things the hard way.)
I = P/A
I = (Etotal/t)/A
I = (NEphoton/t)/A
=>N = AIt/Ephoton
=>N = (1.8x10-9x25x15x60)/ 5.967x10-19
=>N = 4.05x10-5/5.967x10-19
=>N = 6.79x1013
b.iii.The time taken for sunlight to erase the chip will be greater.
This is because only a proportion of the 25W/m2 from sunlight is
ultraviolet and it would therefore take longer for the semiconductor
to absorb the required number of photons.
29.a.i. To calculate x and y use conservation of atomic and mass number.
Atomic Number
Total LHS = Total RHS
88 = y + 2
y = 88 - 2
y = 86
Mass Number
Total LHS = Total RHS
226 = x + 4
x = 226 - 4
x = 222
222
Rn
86
a.ii. Energy is released in this reaction because the mass
of the products is less than that of the radium nucleus.
a.iii.Mass LHS
3.75428x10-25kg
Mass RHS
(3.68771x10-25 + 6.64832x10-27)kg = 3.7541932x10-25kg
Mass defect(DM) = Mass LHS - Mass RHS
DM = 3.75428x10-25 - 3.7541932x10-25
DM = 8.68x10-30kg
E = DMC2
E = 8.68x10-30x(3x108)2
E = 7.812x10-13J
b. Ekfinal = Ekinitial + Ekgain
Ekfinal = 1/2[mvinitial2]
Ekfinal = 1/2[6.64832x10-27x(1.5x107)2]
Ekfinal = 7.47936x10-13J
Ekgain = qV
q = charge on alpha particle = +2e = 2x1.6x10-19 = 3.2x10-19C
V = accelerating potential difference = 25kV
Ekgain = 3.2x10-19x25000
Ekgain = 8x10-15J
Ekfinal = 7.47936x10-13 + 8x10-15
Ekfinal = 7.55936x10-13J
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Return to past paper index page.


Pbottom = Ptop + rgh Pbottom = (108350 + 1000x9.8x0.3)Pa Pbottom = (108350 + 2940)Pa Pbottom = 111290Pa b.
Fupthrust = Fbottom-Ftop Fbottom = PbottomA Fbottom = 111290x0.4 = 44516N Ftop = PtopA Ftop = 108350x0.4 = 43340N Fupthrust = 44516-43340 Fupthrust = 1176N c. As the density of sea water is greater than that of fresh water, the additional pressure, due to the fluid, acting on the lower surface will increase. This will increase the upthrust. 24.a. To calculate the capacitance use the mean values of charge and voltage. C = Q/V C = (32/2.56)mF C=12.5mF The percentage error in capacitance value can be taken to be equal to that of largest individual percentage error. % error in voltage = (0.01/2.56)x100 = 0.39% % error in charge = (1/32)x100 = 3.125% C=12.5mF+-3.125% OR 3.125% of 12.5mF = 0.39mF => C = (12.5+-0.4)mF NB/ Only quote the error to the same number of decimal places as the capacitance value. b.i. The maximum energy is stored in the capacitor when the voltage across the capacitor is equal to the supply voltage. Vc= 12V C = 2200x10-6 E = ? E = 1/2(QVc) Q = CVc =>E = 1/2(CVc2) E = 0.5(2200x10-6x122) E = 0.1584J b.ii.(A) When the switch is opened the capacitor discharges through the resistor and relay coil. The discharge current magnetises the coil closing the switch in the lamp circuit, causing the lamp to light. As the discharge current gradually falls the coil loses its magnetism and the switch in the lamp circuit opens. When this happens the lamp goes off. (B) Increasing the value of the capacitor increases the discharge time. The energy stored in the capacitor is also greater. This means that the lamp will stay lit for longer. 25.a.i. When used to produce a voltage the diode is said to be in photo voltaic mode. a.ii. Light produces electron hole pairs in the depletion layer of the pn-junction. a.iii.The voltmeter reading increases as the intensity of the light increases. b.i. The emf is equal to the open circuit voltage. emf = 0.508V b.ii. r = Vlost/I r = (0.508-0.040)/1.08x10-3 r = 0.468/1.08x10-3 r = 433.3W Note: The answer to part (b.ii.) is too high to be realistic. For this reason a correction was made to the values used during the exam. However, the above answer does not use the corrected value. c. Decreasing the value of the load resistor will increase the current in the circuit. This will increase the "lost" volts (Vlost=Ir). Voltmeter reading = emf-Vlost This explains the lower reading on the voltmeter when the switch is closed. 26.a.i. Period(T) = 4x2.5ms = 10ms frequency(f) = 1/T f = 1/10x10-3 f = 100Hz a.ii. Vpeak = 2x5 = 10V Vrms = Vpeak/SQRT2 Vrms = 10/1.414 Vrms = 7.07V Irms = Vrms/R Irms = 7.07/200 Vrms = 0.035A b. The amplitude of the voltage across the resistor is reduced because there is a voltage drop across the diode. The negative half of the voltage cycle is removed because the diode only conducts when it is forward biased. 27.a. The intensity of radiation is equal to the incident power per unit area. I = P/A b. By keeping the light meter a constant distance from X you are justified in stating that any change in the recorded intensity is a result of changing q. If the distance was altered a change in intensity could be the result of a diverging beam. c.i. The critical angle is found by noting the incident angle at which the reflected intensity reaches a maximum. q = 42o c.ii. nglass = 1/sinqcritical nglass = 1/sin42o nglass = 1.49 c.iii.The intensity of ray T will decrease as angle q is increased upto 42o. At angles equal to and above 42o the intensity of ray T will fall to zero, as the incident ray will be totally internally reflected. 28.a.i. Photoelectric emission is the term used to describe the process by which an electron bound in an atom can absorb enough energy from a single photon to escape, or be emitted, from the atom. a.ii. Threshold frequency a.iii.As the intensity of the radiation is increased there are more incident photons on the metal. Consequently, more electrons can absorb energy from the incident radiation. This will result in more emitted electrons which is consistent with the increased current. 28.b.i. Ephoton = hf Ephoton = 6.63x10-34x9.0x1014 Ephoton = 5.967x10-19J b.ii. Etotal = NEphoton N = Etotal/Ephoton N = 40.5x10-6/5.967x10-19 N = 6.79x1013 OR (If you like doing things the hard way.) I = P/A I = (Etotal/t)/A I = (NEphoton/t)/A =>N = AIt/Ephoton =>N = (1.8x10-9x25x15x60)/ 5.967x10-19 =>N = 4.05x10-5/5.967x10-19 =>N = 6.79x1013 b.iii.The time taken for sunlight to erase the chip will be greater. This is because only a proportion of the 25W/m2 from sunlight is ultraviolet and it would therefore take longer for the semiconductor to absorb the required number of photons. 29.a.i. To calculate x and y use conservation of atomic and mass number. Atomic Number Total LHS = Total RHS 88 = y + 2 y = 88 - 2 y = 86 Mass Number Total LHS = Total RHS 226 = x + 4 x = 226 - 4 x = 222 222 Rn 86 a.ii. Energy is released in this reaction because the mass of the products is less than that of the radium nucleus. a.iii.Mass LHS 3.75428x10-25kg Mass RHS (3.68771x10-25 + 6.64832x10-27)kg = 3.7541932x10-25kg Mass defect(DM) = Mass LHS - Mass RHS DM = 3.75428x10-25 - 3.7541932x10-25 DM = 8.68x10-30kg E = DMC2 E = 8.68x10-30x(3x108)2 E = 7.812x10-13J b. Ekfinal = Ekinitial + Ekgain Ekfinal = 1/2[mvinitial2] Ekfinal = 1/2[6.64832x10-27x(1.5x107)2] Ekfinal = 7.47936x10-13J Ekgain = qV q = charge on alpha particle = +2e = 2x1.6x10-19 = 3.2x10-19C V = accelerating potential difference = 25kV Ekgain = 3.2x10-19x25000 Ekgain = 8x10-15J Ekfinal = 7.47936x10-13 + 8x10-15 Ekfinal = 7.55936x10-13J