
Solutions to SQA examination
1996 Higher Grade Physics
Paper I Solutions
Return to past paper index page.
1. C 11. E 21. C
2. C 12. D 22. E
3. B 13. A 23. A
4. D 14. D 24. B
5. B 15. D 25. E
6. B 16. C 26. A
7. E 17. A 27. A
8. C 18. E 28. B
9. C 19. E 29. B
10.C 20. C 30. E
31. Step one : calculate the time the arrow takes to reach the target
using the fact that the horizontal velocity is constant.
t = shor/vhor
t = 30/100
t = 0.3s
Step two : calculate the vertical displacement of the ball in this time.
uver= 0m/s
t = 0.3s
a = -9.8m/s/s
sver = ?
sver = ut + 1/2(at2)
sver = 0 + 1/2(-9.8x0.32)
sver = -0.441m
Step three : calculate the radius of the target.
r = 1.5-0.9
r = 0.6m
As the arrow falls less than the radius of the target it hits
the target.
32.a.i.
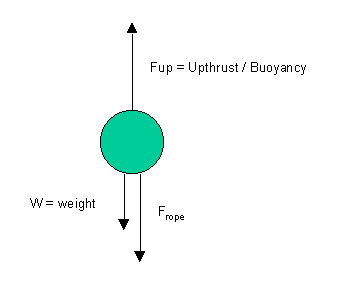 a.ii. Frope = Tension(T)
As the rope is stationary the forces acting on the buoy are balanced.
Fup = w + T
Fup = 50 + 1200
Fup = 1250N
b.
a.ii. Frope = Tension(T)
As the rope is stationary the forces acting on the buoy are balanced.
Fup = w + T
Fup = 50 + 1200
Fup = 1250N
b.
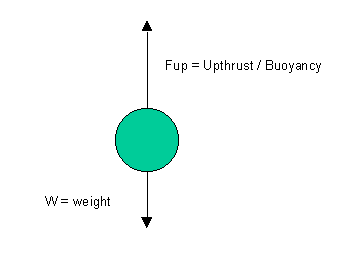 The buoyancy force is not dependent on depth. Therefore, the buoyancy
force is as calculated in part a.ii.(1250N).
33.
The buoyancy force is not dependent on depth. Therefore, the buoyancy
force is as calculated in part a.ii.(1250N).
33.
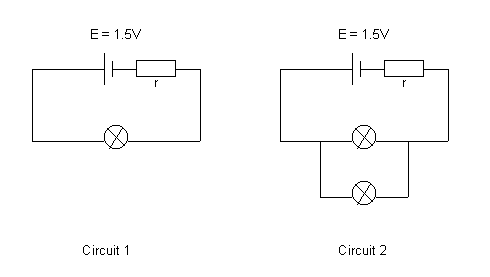 In circuit 1 the total resistance in the circuit is equal
to the sum of the internal resistor(r) and the resistance
of the bulb (Rbulb).
Rtotal = r + Rbulb
In circuit 2 the total resistance in the circuit is equal
to the sum of the internal resistor(r) and the resistance
of the two bulbs in parallel.
Rtotal = r + Rbulb/2
The total resistance in circuit 2 is less than that in circuit 1. Thus
the current(I) flowing through the internal resistor in circuit 2 is greater.
The "lost" voltage (Vlost=Ir) across the internal resistor is
therefore greater in circuit 2. This means the voltage across the lamps
(Vlamp = E -Ir) is less in circuit 2 reducing the brightness of the
lamps.
34.a. Vrms = Vpk/21/2
Vrms = 12/1.414
Vrms = 8.5V
b. P = Irms2
Irms = Vrms/R
Irms = 8.5/4
Irms = 2.12A
P = 2.122x4
P = 18W
35. dsinq = nl
d = 1/2.5x105 = 4x10-6m
l = 600x10-9m
n = 1
q = ?
sinq = nl/d
sinq = 1x600x10-9/4x10-6
sinq = 0.15
q = 8.63o
36.a. Possible transitions : E3 -> E2
E3 -> E1
E3 -> E0
E2 -> E1
E2 -> E0
E1 -> E0
b. A total of 6 lines are in the spectrum.
Low frequency radiation will be produced when the transition
is between energy levels with a small energy gap.
The smallest energy gap is between levels E3 and E2.
c. Transitions between certain states will be more frequent than others.
The more frequent a transition, the more intense the spectral line will be.
37. Ek = Ephoton - Ework function
Ephoton = hf = hc/l
Ephoton = (6.63x10-34x3x108)/5.4x10-7
Ephoton = 3.68x10-19J
Ek = 3.7x10-19 - 2.9x10-19
Ek = 0.8x10-19
In circuit 1 the total resistance in the circuit is equal
to the sum of the internal resistor(r) and the resistance
of the bulb (Rbulb).
Rtotal = r + Rbulb
In circuit 2 the total resistance in the circuit is equal
to the sum of the internal resistor(r) and the resistance
of the two bulbs in parallel.
Rtotal = r + Rbulb/2
The total resistance in circuit 2 is less than that in circuit 1. Thus
the current(I) flowing through the internal resistor in circuit 2 is greater.
The "lost" voltage (Vlost=Ir) across the internal resistor is
therefore greater in circuit 2. This means the voltage across the lamps
(Vlamp = E -Ir) is less in circuit 2 reducing the brightness of the
lamps.
34.a. Vrms = Vpk/21/2
Vrms = 12/1.414
Vrms = 8.5V
b. P = Irms2
Irms = Vrms/R
Irms = 8.5/4
Irms = 2.12A
P = 2.122x4
P = 18W
35. dsinq = nl
d = 1/2.5x105 = 4x10-6m
l = 600x10-9m
n = 1
q = ?
sinq = nl/d
sinq = 1x600x10-9/4x10-6
sinq = 0.15
q = 8.63o
36.a. Possible transitions : E3 -> E2
E3 -> E1
E3 -> E0
E2 -> E1
E2 -> E0
E1 -> E0
b. A total of 6 lines are in the spectrum.
Low frequency radiation will be produced when the transition
is between energy levels with a small energy gap.
The smallest energy gap is between levels E3 and E2.
c. Transitions between certain states will be more frequent than others.
The more frequent a transition, the more intense the spectral line will be.
37. Ek = Ephoton - Ework function
Ephoton = hf = hc/l
Ephoton = (6.63x10-34x3x108)/5.4x10-7
Ephoton = 3.68x10-19J
Ek = 3.7x10-19 - 2.9x10-19
Ek = 0.8x10-19
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Return to past paper index page.


a.ii. Frope = Tension(T) As the rope is stationary the forces acting on the buoy are balanced. Fup = w + T Fup = 50 + 1200 Fup = 1250N b.
The buoyancy force is not dependent on depth. Therefore, the buoyancy force is as calculated in part a.ii.(1250N). 33.
In circuit 1 the total resistance in the circuit is equal to the sum of the internal resistor(r) and the resistance of the bulb (Rbulb). Rtotal = r + Rbulb In circuit 2 the total resistance in the circuit is equal to the sum of the internal resistor(r) and the resistance of the two bulbs in parallel. Rtotal = r + Rbulb/2 The total resistance in circuit 2 is less than that in circuit 1. Thus the current(I) flowing through the internal resistor in circuit 2 is greater. The "lost" voltage (Vlost=Ir) across the internal resistor is therefore greater in circuit 2. This means the voltage across the lamps (Vlamp = E -Ir) is less in circuit 2 reducing the brightness of the lamps. 34.a. Vrms = Vpk/21/2 Vrms = 12/1.414 Vrms = 8.5V b. P = Irms2 Irms = Vrms/R Irms = 8.5/4 Irms = 2.12A P = 2.122x4 P = 18W 35. dsinq = nl d = 1/2.5x105 = 4x10-6m l = 600x10-9m n = 1 q = ? sinq = nl/d sinq = 1x600x10-9/4x10-6 sinq = 0.15 q = 8.63o 36.a. Possible transitions : E3 -> E2 E3 -> E1 E3 -> E0 E2 -> E1 E2 -> E0 E1 -> E0 b. A total of 6 lines are in the spectrum. Low frequency radiation will be produced when the transition is between energy levels with a small energy gap. The smallest energy gap is between levels E3 and E2. c. Transitions between certain states will be more frequent than others. The more frequent a transition, the more intense the spectral line will be. 37. Ek = Ephoton - Ework function Ephoton = hf = hc/l Ephoton = (6.63x10-34x3x108)/5.4x10-7 Ephoton = 3.68x10-19J Ek = 3.7x10-19 - 2.9x10-19 Ek = 0.8x10-19